Spring IOC
2024/09/04
posted in
Spring
2024/09/04
posted in
Spring
IOC is also known as dependency injection(DI). It is a process whereby objects define their dependencies (that is, the other objects they work with) only through constructor arguments, arguments to a factory method, or propertied that are set on the object instance after it is constructed or returned from a factory method. The container then injects those dependencied when it creates the bean. This process is fundamentally the inverse (hence the namem, Inversion of Control) of the bean itself controlling the instantiation or location of its dependencies by using direct construction of classes or a mechanism such as the Service Locator pattern.
IoC(Inversion of Control) 也称为依赖注入(dependency injection, DI)。它是一个==对象定义依赖关系的过程==,也就是说,对象只通过构造函数参数、工厂方法的参数或对象实例构造或从工厂方法返回后在对象实例上设置的属性来定义它们所使用的其他对象。然后==容器在创建bean时注入这些依赖项==。这个过程基本上是bean的逆过程,因此称为控制反转(IoC)
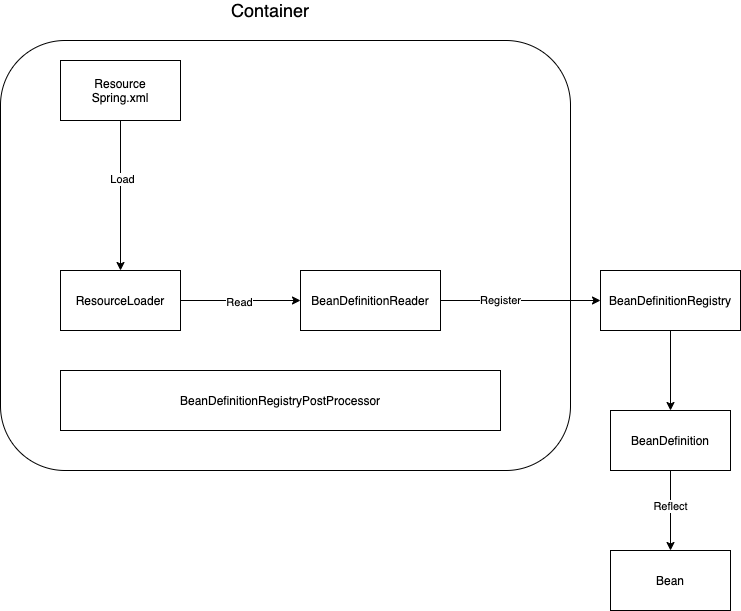
IoC容器:通过容器统一对象的构建方式,并且自动维护对象的依赖关系。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.bean.User"/>
</beans>
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
@ImportResource("spring.xml")
public class AppConfig {
}
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
public class MyFactroyBean implements FactoryBean {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return new User();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return User.class;
}
}
AbstractBeanFactory#getObjectForBeanInstance
!(beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean) || BeanFactoryUtils.isFactoryDereference(name)
@ComponentScan默认扫描: @Component, @Repository,@Service, @Controller
@ComponentScan("com.carl.service")
public class AppConfig {
}
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.carl.service",excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,value = {Service.class}),
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,value = {User.class})
})
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.carl.service",includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,value = {CustomTypeFilter.class})
},useDefaultFilters = false)
FilterType.CUSTOM实现自定义过滤规则
public class CustomTypeFilter implements TypeFilter {
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
ClassMetadata classMetadata = metadataReader.getClassMetadata();
if (classMetadata.getClassName().contains("Service")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public User user(){
return new User();
}
@Bean
public UserService userService(){
// 调用其他@Bean方法
return new UserService(user());
}
}
配置@Configuration与不配置的区别:
不配置@Configuration当内部method bean发生彼此依赖的时候会导致多例
@Import(value = MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)
public class AppConfig {
}